3. Flow Hoods for Air Balancing
- An air-balancing hood measures how much air each register delivers
- Using flow hoods allows contractors to verify if supply and return airflows are correctly matched and balanced throughout the home
- Balancing air distribution ensures even heating and cooling, reducing hot and cold spots.
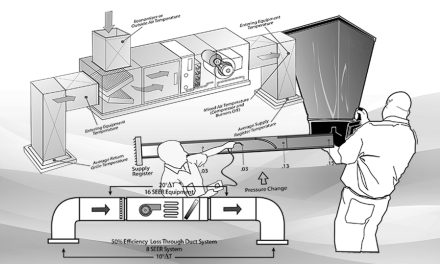
4. Duct Leakage Testing

with a “Roomulator” and a micromanometer.
- Using a duct leakage test, technicians can measure leakage rates in the duct system
- Excessive duct leakage leads to significant energy losses and comfort issues
- Sealing ducts using mastic and proper insulation improves airflow efficiency and reduces system strain.
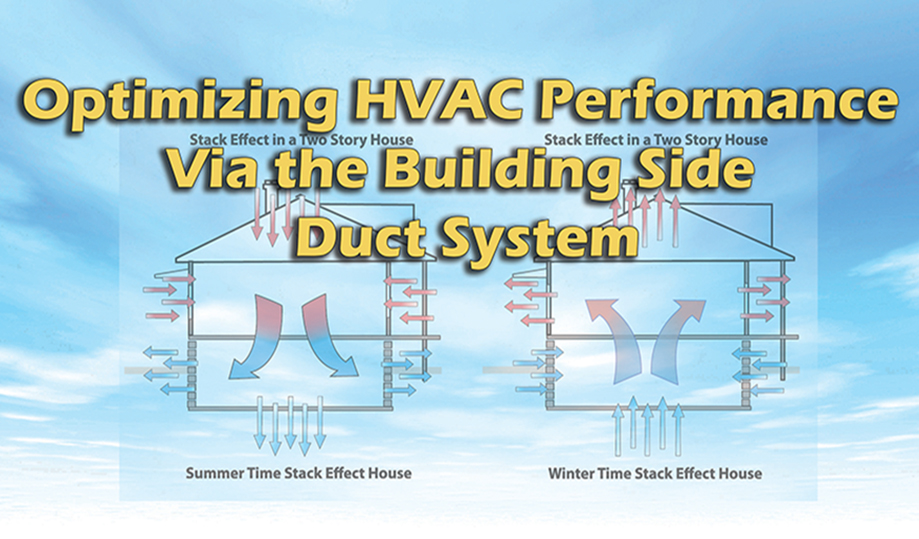
Addressing Common Airflow Problems
Room Pressure Imbalances: When doors to bedrooms are closed, those rooms become pressurized if they lack return air pathways. This forces conditioned air out through unintended gaps, increasing system inefficiencies. Solutions include:
- Installing jumper ducts to provide a direct return air path
- You should add transfer grilles to equalize pressure between rooms and hallways
- Enlarging return pathways to improve airflow and balance indoor pressure.

easier to take, especially with LiDAR
technology for use in room sizing
for load calculations.
Duct Design Issues: Many duct systems are undersized, kinked, or improperly routed, leading to static pressure problems. When static pressure is too high, the blower works harder, reducing efficiency and increasing wear on components.
- Always verify duct sizing using industry-standard calculations
- Seal ducts to minimize leakage and ensure efficient airflow
- Ensure adequate return pathways for unrestricted airflow to maintain system balance
- Avoid long, restrictive flex duct runs because they can significantly reduce airflow and efficiency.
Combustion Safety Risks: Pressure imbalances can backdraft combustion appliances, leading to dangerous carbon monoxide buildup. Testing combustion appliance zones for depressurization is critical, especially when modifying duct systems.
- Always test for back drafting when adjusting pressure dynamics
- Ensure proper ventilation and fresh air intakes for safe combustion
- Monitor carbon monoxide levels in homes with natural draft appliances.
Practical Steps to Implement Testing & Air Balancing
For HVAC contractors looking to incorporate performance testing into their service offerings, the following steps will provide a solid foundation:
- Invest in Proper Testing Equipment
- A micro-manometer and air-balancing hood are essential for diagnosing airflow problems
- A blower door is valuable for whole-house performance assessments
- Tools like thermal imaging cameras can help visualize heat loss and air infiltration points.
Click Below for the Next Page:











Recent Comments